Top Hip Replacement Surgery Doctor in Delhi NCR
Specialities

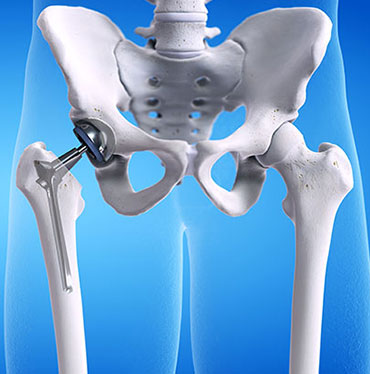
What is Hip Replacement Surgery?
Hip replacement surgery, also known as hip arthroplasty, is a medical procedure that involves removing a damaged or worn-out hip joint and replacing it with an artificial joint, known as a prosthesis. This procedure is commonly recommended for individuals suffering from chronic hip pain or dysfunction caused by conditions such as arthritis, hip fractures, or other hip joint diseases.
When is Hip Replacement Surgery Recommended?
Hip replacement surgery is typically recommended when conservative treatments (like medication, physical therapy, or lifestyle changes) are no longer effective in relieving pain or improving hip function. It is usually considered when the following conditions are present:
- Severe Hip Pain: Persistent pain that limits daily activities, not relieved by medication or therapy.
- Joint Stiffness: significant loss of flexibility, making movement difficult.
- Limited Mobility: Difficulty walking, climbing stairs, or performing basic tasks.
- Ineffective Non-Surgical Treatments: No relief from medications, physical therapy, or injections.
- Hip Fractures: Poor healing of hip fractures, especially in older adults.
- Severe Arthritis: Advanced osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis with worn-out cartilage.
- Decreased Quality of Life: Inability to participate in activities or social events.
- Pain Disrupting Sleep: Hip pain severe enough to affect sleep and rest.
If any of these apply to you, consult an orthopedic surgeon for a detailed evaluation.
How Hip Replacement Surgery is Beneficial
Hip replacement surgery offers life-changing benefits for individuals suffering from chronic hip pain and limited mobility. By replacing the damaged hip joint with an artificial one, patients experience significant pain relief, improved mobility, and a better quality of life. It allows individuals to return to normal activities, restore independence, and enjoy long-lasting results, often with minimal complications.
- Pain Relief: Reduces or eliminates chronic hip pain.
- Improved Mobility: Restores flexibility and ease of movement.
- Enhanced Quality of Life: Increases participation in daily activities and hobbies.
- Long-Term Durability: Results can last 15–20 years or more.
- Increased Independence: Reduces reliance on assistive devices.
- Restored Functionality: Brings the hip joint back to normal function.
- High Success Rate: Most patients experience significant improvement.
- Minimal Risk of Complications: With modern techniques, complications are rare.
Types of Hip Replacement Surgery:
There are several types of hip replacement surgery, each tailored to the patient’s specific condition, the extent of damage to the hip joint, and the surgeon’s preferred technique. The most common types include total hip replacement, partial hip replacement, minimally invasive surgery, anterior hip replacement, and hip resurfacing. Each type offers distinct benefits, depending on the patient's age, activity level, and the condition of the hip joint.
- Total Hip Replacement (THR): Replaces both the femoral head (ball) and the acetabulum (socket).
- Partial Hip Replacement: Replaces only the femoral head, leaving the socket intact.
- Minimally Invasive Hip Replacement: Uses smaller incisions to reduce recovery time and muscle damage.
- Anterior Hip Replacement: Accesses the joint from the front, reducing muscle disruption.
- Hip Resurfacing: Caps the femoral head with a metal shell, preserving more bone structure.
More About Hip Replacement Surgery
Hip replacement surgery is a highly effective procedure for individuals suffering from chronic hip pain due to conditions such as osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, hip fractures, or other hip joint diseases. The goal of the surgery is to replace the damaged or worn-out parts of the hip joint with artificial components, providing pain relief, restoring mobility, and improving the overall quality of life. Hip replacement can be done in various ways, depending on the specific needs of the patient and the extent of joint damage.
The surgery is generally recommended when conservative treatments, such as medications, physical therapy, or injections, fail to provide sufficient relief. It is particularly beneficial for people who have significant pain or difficulty in performing daily activities such as walking, climbing stairs, or sitting for extended periods. With advancements in surgical techniques, the procedure has become more precise and effective, ensuring better outcomes and faster recovery times.
After surgery, patients typically undergo physical therapy to regain strength, flexibility, and movement in the hip joint. Most individuals are able to resume normal activities within a few weeks to a few months, though high-impact activities like running may be restricted. The benefits of hip replacement surgery include long-term pain relief, improved function, and an enhanced quality of life.
Treatment
Treatment for hip problems ranges from non-surgical options to surgery, depending on the severity of the condition. Non-surgical treatments include medications for pain relief, physical therapy to strengthen muscles and improve mobility, assistive devices like canes or walkers, and lifestyle modifications such as weight management. When these options are ineffective, surgical treatments such as hip arthroscopy, total or partial hip replacement, and hip resurfacing may be considered. For patients with less severe issues, alternative treatments like stem cell therapy or platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections may offer additional options. Surgery is typically recommended when pain and functional limitations significantly impact daily life.
Recovery
Recovery after hip replacement surgery typically involves several stages:
- Hospital Stay (2–4 Days): Patients are monitored for pain management and initial recovery.
- Physical Therapy: Starts right after surgery to regain mobility, with increasing intensity over 6–12 weeks.
- Activity Restrictions: Use of mobility aids like crutches or walkers, avoiding certain movements to prevent complications.
- Return to Normal Activities (6–12 Weeks): Light activities like walking and driving can be resumed.
- Long-Term Care: Regular follow-ups with the surgeon and monitoring of the prosthesis to ensure longevity.
With proper care, most patients experience significant pain relief and improved mobility, returning to everyday activities.
